[MathJax off]
2 Posets
2.1 The Poset type
Every poset has a Set of points and an Ordering.
2.1-1 Ordering
‣ Ordering( X ) | ( operation ) |
A function computing the order of the poset \(X\). The truth value of the expression \(x\geq y\) is Ordering(X)(x,y).
gap> W:=TheWallet();
<finite poset of size 11>
gap> o:=Ordering(W);
function( x, y ) ... end
gap> o(1,5);
true
gap> o(1,7);
false
2.1-2 Set
The set of points of \(X\).
gap> Set(TheWallet());
[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
2.1-3 \=
‣ \=( X_1, X_2 ) | ( operation ) |
Two posets are equal if the sets of points are equal and the ordering is the same.
gap> P:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1,2,3,4],[]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> Q:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1,2,3,4], [[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> P = Q;
false
gap> P = P;
true
2.1-4 Size
The size (number of points) of \(X\).
gap> S4:=MinimalFiniteModelSphere(4);;
gap> Size(S4);
10
2.1-5 Iterator
‣ Iterator( X ) | ( operation ) |
An iterator for the set of points of \(X\).
2.1-6 \in
‣ \in( x, X ) | ( operation ) |
The truth value of \(x\in X\).
gap> 11 in TheWallet();
true
gap> 12 in TheWallet();
false
gap> S2:=MinimalFiniteModelSphere(2);;
gap> IdentityMap(S2) in HomPosets(S2,S2);
true
2.2 Examples of posets
2.2-1 EmptyPoset
‣ EmptyPoset( ) | ( operation ) |
The empty poset.
gap> P:=EmptyPoset();
<finite poset of size 0>
2.2-2 MinimalFiniteModelSphere
‣ MinimalFiniteModelSphere( n ) | ( operation ) |
The minimal finite model of the \(n\)-sphere \(S^n\) [Bar11, Section 3.2].
gap> S1:=MinimalFiniteModelSphere(1);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> S4:=MinimalFiniteModelSphere(4);
<finite poset of size 10>
2.2-3 TheWallet
‣ TheWallet( ) | ( operation ) |
The Wallet is a homotopically trivial poset on \(11\) points which is not contractible [Bar11, Example 4.2.1].
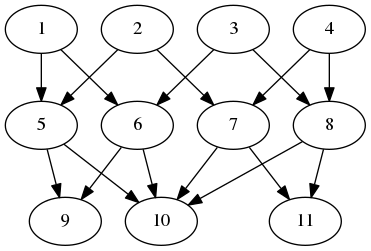
gap> W:=TheWallet();
<finite poset of size 11>
gap> Set(W);
[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
gap> PosetHomology(W);
[ [ 0 ], [ ], [ ] ]
2.2-4 TheTriangle
‣ TheTriangle( ) | ( operation ) |
The Triangle is a poset on 19 points, see [Fer17, Example 2.2.7].
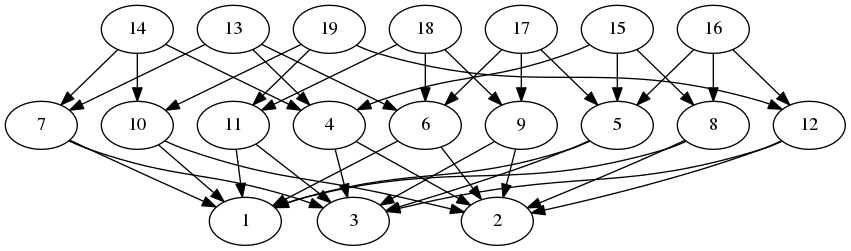
2.2-5 FiniteModelProjectivePlane
‣ FiniteModelProjectivePlane( ) | ( operation ) |
A finite model of the projective plane \(\mathbb{R}P^2\) [Bar11, Example 7.1.1].
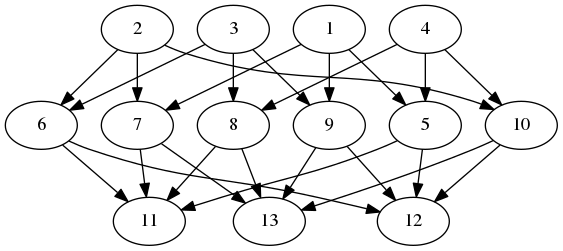
gap> RP2:=FiniteModelProjectivePlane();
<finite poset of size 13>
gap> FundamentalGroup(RP2);
#I there are 1 generator and 1 relator of total length 2
<fp group on the generators [ f1 ]>
gap> Size(last);
2
gap> PosetHomology(RP2);
[ [ 0 ], [ 2 ], [ ] ]
2.3 Plotting posets
To produce plots, the functions in this section need the software graphviz (https://www.graphviz.org) to be installed.
2.3-1 DotCode
‣ DotCode( X, options ) | ( function ) |
Returns a string in the DOT language representing the Hasse diagram of the poset X. The parameter options allows to customize the plot.
2.3-2 DotCodeToFile
‣ DotCodeToFile( code, filename ) | ( function ) |
This function takes code in the DOT language and saves the plot at filename.
2.3-3 PlotHasseDiagram
‣ PlotHasseDiagram( X, filename ) | ( function ) |
This function plots the Hasse diagram of X using the command dot. The plot is displayed and stored at filename. Many file extensions are supported.
gap> W:=TheWallet();;
gap> PlotHasseDiagram(W,"wallet.pdf");
2.3-4 PlotMorseMatching
‣ PlotMorseMatching( X, M, filename ) | ( function ) |
This function plots a Morse matching using the command dot. The matched edges are reversed and colored red. The plot is displayed and stored at filename.
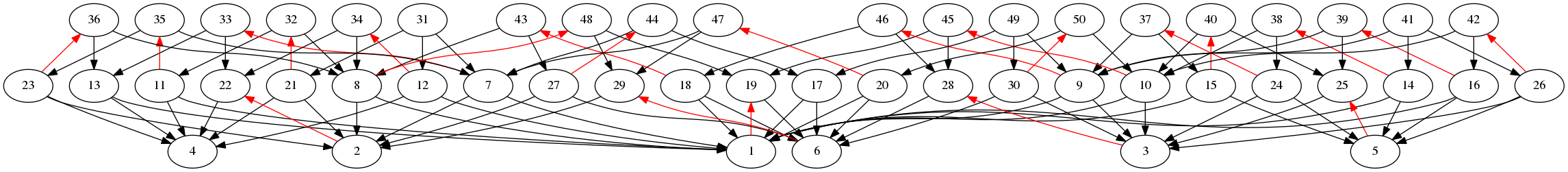
gap> F:=FreeGroup("x","y");;
gap> AssignGeneratorVariables(F);;
gap> G:=F/[x^3,y^3,Comm(x,y)];;
gap> P:=PosetFpGroup(G);
<finite poset of size 50>
gap> M:=GreedySpanningMatching(P);;
gap> PlotMorseMatching(P,M,"matching.pdf");
2.4 Homomorphisms
2.4-1 IdentityMap
‣ IdentityMap( X ) | ( attribute ) |
The identity \(1_X\colon X\to X\).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2], [4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> id:=IdentityMap(A);
<order preserving map>
gap> 1^id;
1
gap> 2^id;
2
gap> 3^id;
3
gap> 4^id;
4
2.4-2 CompositionPosetHomomorphisms
‣ CompositionPosetHomomorphisms( f, g ) | ( operation ) |
‣ CompositionPosetHomomorphismsNC( f, g ) | ( operation ) |
‣ \*( f, g ) | ( operation ) |
The composition \(f\circ g\).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2], [4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> id:=IdentityMap(A);
<order preserving map>
gap> f:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,A, [2,1,4,3]);
<order preserving map>
gap> g:=CompositionPosetHomomorphisms(f,id);
<order preserving map>
gap> g = f;
true
gap> f2:=CompositionPosetHomomorphisms(f,f);
<order preserving map>
gap> f2 = id;
true
gap> h:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(EmptyPoset(),A,[]);
<order preserving map>
gap> CompositionPosetHomomorphisms(h,f);
fail
The composition \(f\circ g\) without any checks. The composition \(g\circ f\).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2], [4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> id:=IdentityMap(A);
<order preserving map>
gap> f:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,A, [2,1,4,3]);
<order preserving map>
gap> f*f = IdentityMap(A);
true
gap> f*id = f;
true
2.4-3 SourceMap
‣ SourceMap( f ) | ( operation ) |
The source \(X\) of a map \(f\colon X\to Y\).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2], [4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> f:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,A, [2,1,4,3]);
<order preserving map>
gap> SourceMap(f) = A;
true
2.4-4 TargetMap
‣ TargetMap( f ) | ( operation ) |
The target \(Y\) of a map \(f\colon X\to Y\).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2], [4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> f:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,A, [2,1,4,3]);
<order preserving map>
gap> TargetMap(f) = A;
true
2.4-5 UnderlyingFunction
‣ UnderlyingFunction( f ) | ( attribute ) |
A GAP function computing f as a set function.
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2], [4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> f:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,A, [2,1,4,3]);
<order preserving map>
gap> uf:=UnderlyingFunction(f);
function( x ) ... end
gap> uf(1);
2
gap> uf(2);
1
2.4-6 Inverse
‣ Inverse( f ) | ( attribute ) |
‣ InverseImmutable( f ) | ( attribute ) |
The inverse of the isomorphism f.
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> B:=PosetByCoveringRelations([5..8], [[7,5],[7,6],[8,5],[8,6]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> h:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,B,[5,6,7,8]);
<order preserving map>
gap> inv1:=Inverse(h);
<order preserving map>
gap> inv2:=InverseImmutable(h);
<order preserving map>
gap> inv1 = inv2;
true
2.4-7 ImageMap
‣ ImageMap( f ) | ( operation ) |
The image \(f(X)\) of a map \(f\colon X\to Y\), given as a subposet of \(Y\).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> B:=PosetByCoveringRelations([5..8], [[7,5],[7,6],[8,5],[8,6]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> h:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,B,[5,6,7,8]);
<order preserving map>
gap> ImageMap(h);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> last = B;
true
2.4-8 ImageMap
‣ ImageMap( f, x ) | ( operation ) |
‣ \^( x, f ) | ( operation ) |
The image \(f(x)\) of an element \(x\in X\) by the map \(f\colon X \to Y\).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> B:=PosetByCoveringRelations([5..8], [[7,5],[7,6],[8,5],[8,6]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> h:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,B,[5,6,7,8]);
<order preserving map>
gap> ImageMap(h,1);
5
gap> ImageMap(h,3);
7
The image \(f(x)\) of an element \(x\in X\) by the map \(f\colon X \to Y\).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> B:=PosetByCoveringRelations([5..8], [[7,5],[7,6],[8,5],[8,6]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> h:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,B,[5,6,7,8]);
<order preserving map>
gap> 1^h;
5
gap> 3^h;
7
2.4-9 \*
‣ \*( L, f ) | ( operation ) |
Given a list \(L\) of poset homomorphisms, it return the list of the compositions \(f\circ g\) for \(g\in L\).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);;
gap> B:=PosetByCoveringRelations([5..8], [[7,5],[7,6],[8,5],[8,6]]);;
gap> f:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,A, [2,1,4,3]);;
gap> h:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,B,[5,6,7,8]);;
gap> [h,f] * f;
[ fail, <order preserving map> ]
gap> [Inverse(h), f] * h;
[ <order preserving map>, <order preserving map> ]
2.4-10 \*
‣ \*( f, L ) | ( operation ) |
Given a list \(L\) of poset homomorphisms, it return the list of the compositions \(g\circ f\) for \(g\in L\).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);;
gap> B:=PosetByCoveringRelations([5..8], [[7,5],[7,6],[8,5],[8,6]]);;
gap> f:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,A, [2,1,4,3]);;
gap> h:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,B,[5,6,7,8]);;
gap> f *[h,f];
[ <order preserving map>, <order preserving map> ]
2.4-11 \^
‣ \^( f, n ) | ( operation ) |
Returns \(f^n\). If \(n=0\) returns the identity. If \(f\) is an isomorphism \(f^{-1}\) is its inverse.
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);;
gap> f:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,A, [2,1,4,3]);;
gap> f^2;
<order preserving map>
gap> f^-2 = IdentityMap(A);
true
gap> B:=PosetByCoveringRelations([5..8], [[7,5],[7,6],[8,5],[8,6]]);;
gap> h:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,B,[5,6,7,8]);;
gap> h^2;
fail
2.5 Constructing poset homomorphisms in different ways
2.5-1 PosetHomomorphismByFunction
‣ PosetHomomorphismByFunction( X, Y, f ) | ( operation ) |
Creates the order preserving map \(f\colon X\to Y\) defined by the GAP function f.
2.5-2 PosetHomomorphismByFunctionNC
‣ PosetHomomorphismByFunctionNC( X, Y, f ) | ( operation ) |
Creates the order preserving map \(f\colon X\to Y\) defined by the GAP function f without any checks.
2.5-3 PosetHomomorphismByImages
‣ PosetHomomorphismByImages( X, Y, ys ) | ( operation ) |
Creates the order preserving map \(f\colon X\to Y\) defined by \(f(x) = ys[i]\) if i = PositionSorted(Set(X),x).
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);;
gap> B:=PosetByCoveringRelations([5..8], [[7,5],[7,6],[8,5],[8,6]]);;
gap> h:=PosetHomomorphismByImages(A,B,[5,6,7,8]);;
gap> List(Set(A), x->x^h);
[ 5, 6, 7, 8 ]
2.5-4 PosetHomomorphismByMapping
‣ PosetHomomorphismByMapping( X, Y, f ) | ( operation ) |
2.5-5 IsomorphismPosets
‣ IsomorphismPosets( X, Y ) | ( operation ) |
An isomorphism between \(X\) and \(Y\) or fail if the posets are not isomorphic.
gap> A:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1..4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);;
gap> IsomorphismPosets(A,MinimalFiniteModelSphere(1));
<order preserving map>
gap> IsomorphismPosets(A,EmptyPoset());
fail
2.6 Construction of posets
2.6-1 PosetByFunction
‣ PosetByFunction( X, f ) | ( operation ) |
PosetByFunction creates a poset with set of points X and ordering function f. Checks that f defines a reflexive, antisymmetric and transitive relation on X.
gap> G:=AlternatingGroup(5);
Alt( [ 1 .. 5 ] )
gap> S:=AllSubgroups(G);;
gap> P:=PosetByFunction(S, IsSubgroup);
<finite poset of size 59>
gap> Q:=PosetOfSubgroups(G);
<finite poset of size 59>
gap> P = Q;
true
2.6-2 PosetByFunctionNC
‣ PosetByFunctionNC( X, f ) | ( operation ) |
PosetByFunctionNC creates a poset with set of points X and ordering function f without any checks.
gap> G:=AlternatingGroup(5);
Alt( [ 1 .. 5 ] )
gap> S:=AllSubgroups(G);;
gap> start:=Runtime();; P:=PosetByFunction(S,IsSubgroup);; Runtime()-start;
624
gap> start:=Runtime();; Q:=PosetByFunctionNC(S,IsSubgroup);; Runtime()-start;
0
gap> P = Q;
true
2.6-3 PosetByOrderMatrix
‣ PosetByOrderMatrix( M ) | ( operation ) |
Returns the poset \(X\) on \(\{1,\ldots,n\}\) such that \(i\succcurlyeq j\) is given by \(M_{i,j}\).
gap> S1:=MinimalFiniteModelSphere(1);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> M:=OrderMatrix(S1);
[ [ true, false, false, false ], [ false, true, false, false ], [ true, true, true, false ],
[ true, true, false, true ] ]
gap> Q:=PosetByOrderMatrix(M);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> Set(Q);
[ 1 .. 4 ]
gap> IsomorphismPosets(S1,Q);
<order preserving map>
2.6-4 PosetByOrderMatrix
‣ PosetByOrderMatrix( X, M ) | ( operation ) |
Returns the poset on X such that X[i]>X[j] is given by M[i][j].
gap> S1:=MinimalFiniteModelSphere(1);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> M:=OrderMatrix(S1);
[ [ true, false, false, false ], [ false, true, false, false ], [ true, true, true, false ],
[ true, true, false, true ] ]
gap> Set(S1);
[ [ 1, "x" ], [ 1, "y" ], [ 2, "x" ], [ 2, "y" ] ]
gap> P:=PosetByOrderMatrix(["a","b","c","d"],M);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> Set(P);
[ "a", "b", "c", "d" ]
gap> IsomorphismPosets(P,Q);
<order preserving map>
2.6-5 PosetByOrderMatrixNC
‣ PosetByOrderMatrixNC( M ) | ( operation ) |
Returns the poset \(X\) on \(\{1,\ldots,n\}\) such that \(i\succcurlyeq j\) is given by \(M_{i,j}\) without any checks.
2.6-6 PosetByOrderMatrixNC
‣ PosetByOrderMatrixNC( X, M ) | ( operation ) |
Returns the poset on X such that X[i]>X[j] is given by M[i][j] without any checks.
2.6-7 PosetByOrderRelation
‣ PosetByOrderRelation( R ) | ( operation ) |
Creates a Poset poset from a partial order binary relation, see IsPartialOrderBinaryRelation (Reference: IsPartialOrderBinaryRelation).
gap> R2:=BinaryRelationOnPoints([[1,2,3], [2,3], [3]]);
Binary Relation on 3 points
gap> IsPartialOrderBinaryRelation(R2);
true
gap> P:=PosetByOrderRelation(R2);
<finite poset of size 3>
2.6-8 PosetByHasseDiagram
‣ PosetByHasseDiagram( X ) | ( operation ) |
Not implemented.
2.6-9 PosetByCoveringRelations
‣ PosetByCoveringRelations( X, rel ) | ( operation ) |
Creates the poset on X with covering relations given by rel. Each element of rel must be a pair [x,y] representing a covering relation \(x\succ y\).
gap> rel:=[[1,3], [1,4], [2,3], [2,4]];
[ [ 1, 3 ], [ 1, 4 ], [ 2, 3 ], [ 2, 4 ] ]
gap> Q:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1,2,3,4],rel);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> S1:=MinimalFiniteModelSphere(1);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> IsomorphismPosets(S1,Q);
<order preserving map>
2.7 Representations of the ordering
2.7-1 RelationByPoset
‣ RelationByPoset( X ) | ( operation ) |
Turns a poset X into a Relation on [1..n], see Relations (Reference: Relations).
gap> W:=TheWallet();
<finite poset of size 11>
gap> RelationByPoset(W);
<general mapping: <object> -> <object> >
gap> IsPartialOrderBinaryRelation(last);
true
2.7-2 OrderMatrix
‣ OrderMatrix( X ) | ( attribute ) |
The order matrix of X. After calling OrderMatrix comparing two elements of X becomes immediate.
gap> S1:=MinimalFiniteModelSphere(1);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> OrderMatrix(S1);
[ [ true, false, false, false ], [ false, true, false, false ], [ true, true, true, false ],
[ true, true, false, true ] ]
2.7-3 OrderingByIndex
‣ OrderingByIndex( X ) | ( attribute ) |
Returns a two valued function on the set [1..Size(X)]. If X has order matrix, this function valued in \((i,j)\) returns OrderMatrix(X)[i][j]. Otherwise, it returns Ordering(X)(Set(X)[i],Set(X)[j]).
gap> S1:=MinimalFiniteModelSphere(1);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> OrderMatrix(S1);
[ [ true, false, false, false ], [ false, true, false, false ], [ true, true, true, false ],
[ true, true, false, true ] ]
gap> fun:=OrderingByIndex(S1);
function( i, j ) ... end
gap> fun(1,3);
false
gap> fun(3,1);
true
gap> fun(2,2);
true
2.7-4 CoveringRelations
‣ CoveringRelations( X ) | ( attribute ) |
The list of covering relations of X.
gap> W:=TheWallet();
<finite poset of size 11>
gap> Set(W);
[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
gap> CoveringRelations(W);
[ [ 1, 5 ], [ 1, 6 ], [ 2, 5 ], [ 2, 7 ], [ 3, 6 ], [ 3, 8 ], [ 4, 7 ], [ 4, 8 ], [ 5, 9 ], [ 5, 10 ], [ 6, 9 ],
[ 6, 10 ], [ 7, 10 ], [ 7, 11 ], [ 8, 10 ], [ 8, 11 ] ]
2.7-5 UpperCovers
‣ UpperCovers( X ) | ( attribute ) |
Returns the function on X such that its value on an element x in X is the list of the upper covers of x. Recall that given a finite poset \(X\) and an element \(x\in X\), its upper covers are the elements \(y\in X\) such that \(y > x\) and there is no \(z\in X\) such that \(y > z > x\).
gap> W:=TheWallet();
<finite poset of size 11>
gap> Set(W);
[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
gap> CoveringRelations(W);
[ [ 1, 5 ], [ 1, 6 ], [ 2, 5 ], [ 2, 7 ], [ 3, 6 ], [ 3, 8 ], [ 4, 7 ], [ 4, 8 ], [ 5, 9 ], [ 5, 10 ], [ 6, 9 ],
[ 6, 10 ], [ 7, 10 ], [ 7, 11 ], [ 8, 10 ], [ 8, 11 ] ]
gap> fun:=UpperCovers(W);
function( x ) ... end
gap> fun(1);
[ ]
gap> fun(10);
[ 5, 6, 7, 8 ]
gap> fun(5);
[ 1, 2 ]
2.7-6 UpperCovers
‣ UpperCovers( X, x ) | ( operation ) |
Returns the upper covers of the element x in the poset X.
gap> W:=TheWallet();
<finite poset of size 11>
gap> Set(W);
[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]
gap> UpperCovers(W,10);
[ 5, 6, 7, 8 ]
2.7-7 LowerCovers
‣ LowerCovers( X ) | ( attribute ) |
Returns the function on X such that its value on an element x in X is the list of the lower covers of x. Recall that given a finite poset \(X\) and an element \(x\in X\), its lower covers are the elements \(y\in X\) such that \(x > y\) and there is no \(z\in X\) such that \(x > z > y\).
gap> S1:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1,2,3,4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> CoveringRelations(S1);
[ [ 3, 1 ], [ 3, 2 ], [ 4, 1 ], [ 4, 2 ] ]
gap> g:=LowerCovers(S1);
function( x ) ... end
gap> g(2);
[ ]
gap> g(4);
[ 1, 2 ]
2.7-8 LowerCovers
‣ LowerCovers( X, x ) | ( operation ) |
Returns the lower covers of the element x in the poset X.
gap> S1:=PosetByCoveringRelations([1,2,3,4], [[3,1],[3,2],[4,1],[4,2]]);
<finite poset of size 4>
gap> LowerCovers(S1,4);
[ 1, 2 ]
2.7-9 MaximalElements
‣ MaximalElements( X ) | ( attribute ) |
The set of maximal points of \(X\).
gap> G:=AlternatingGroup(5);
Alt( [ 1 .. 5 ] )
gap> SpG:=BrownPoset(G,2);
<finite poset of size 20>
gap> Max:=MaximalElements(SpG);;
gap> Size(Max);
5
gap> List(Max,Order);
[ 4, 4, 4, 4, 4 ]
gap> S:=SylowSubgroup(G,2);;
gap> N:=Normalizer(G,S);;
gap> Index(G,N);
5
gap> Min:=MinimalElements(SpG);;
gap> Size(Min);
15
gap> List(Min,Order);
[ 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ]
2.7-10 MinimalElements
‣ MinimalElements( X ) | ( attribute ) |
The set of minimal points of \(X\).
gap> G:=AlternatingGroup(5);
Alt( [ 1 .. 5 ] )
gap> SpG:=BrownPoset(G,2);
<finite poset of size 20>
gap> Min:=MinimalElements(SpG);;
gap> Size(Min);
15
gap> List(Min,Order);
[ 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ]
2.7-11 MaximumPoset
‣ MaximumPoset( X ) | ( attribute ) |
Returns the maximum of the poset if it exists. Otherwise it returns fail.
gap> P:=CyclicGroup(4);
<pc group of size 4 with 2 generators>
gap> SpG:=BrownPoset(P,2);
<finite poset of size 2>
gap> MaximumPoset(SpG);
Group([ f2, f1 ])
gap> W:=TheWallet();
<finite poset of size 11>
gap> MaximumPoset(W);
fail
2.7-12 MinimumPoset
‣ MinimumPoset( X ) | ( attribute ) |
Returns the minimum of the poset if it exists. Otherwise it returns fail.
gap> P:=SmallGroup(4,2);
<pc group of size 4 with 2 generators>
gap> SpG:=BrownPoset(P,2);
<finite poset of size 2>
gap> MinimumPoset(SpG);
fail
gap> W:=TheWallet();
<finite poset of size 11>
gap> MinimumPoset(W);
fail
2.7-13 IndicesElementsAbove
‣ IndicesElementsAbove( arg ) | ( attribute ) |
2.7-14 IndicesElementsBelow
‣ IndicesElementsBelow( arg ) | ( attribute ) |
2.8 Saving posets
2.8-1 SavePosetAsListsOfElementsBelow
‣ SavePosetAsListsOfElementsBelow( arg1, arg2 ) | ( operation ) |
2.8-2 SavePosetAsOrderMatrix
‣ SavePosetAsOrderMatrix( arg1, arg2 ) | ( operation ) |




